DIY Audiobook
Preface
Love books. But a packed schedule leaves no time for reading. Audiobooks are the rescue. Last year alone managed to listen to 68 of them. Also love not just standalone books but series with rich worlds and well developed characters.
Last week finished listening to another book from a detective series and discovered with horror: the next few books have no audio versions! Though a couple of the final ones in the series do exist as audiobooks. Just like that, by some strange twist of fate, the central part of the story is missing.
The idea of creating my own audio versions came up before when stumbling upon titles without narration. But this time the problem was urgent and pushed me to action.
What You’ll Need
- An ebook in epub format (or txt)
- Python 3+
- ffmpeg
- Calibre CLI
- npx (comes with Node.js)
- A Google Cloud account with billing enabled
- Cloud Text-to-Speech API enabled
Cook book
Preparing the Text
First thought was to just feed the epub into some service and get ready audio. But all existing products either can’t handle large volumes of text or cost too much.
Well, am I not a developer? Let’s figure this out.
First step is converting epub to plain text. If you already have a clean txt file you can skip this.
Calibre CLI works great for conversion:
ebook-convert book.epub book.txtThis gives us book.txt with the full text of the book.
Then open book.txt and remove everything unnecessary: table of contents, foreword, afterword, notes, etc. Only the main text is needed. Everything in this file will be voiced. Listening to extras is boring and wastes precious tokens.
Splitting into Chapters
Next step is splitting the book into chapters. First, the result quality was unknown. Would be a shame to voice the entire book and then realize it sounds bad. Better to be disappointed early. Second, wanted to track costs and not get shocked by the final bill. Spoiler: it was free.
The book was split by chapters with some rules: everything before chapter one goes to prologue. Each chapter file starts with “Chapter N” so the voice reads it out.
Also normalized the text. Cleaned up extra line breaks and spaces to avoid pauses in the narration.
Used a Python script:
Chapter splitting script
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from __future__ import annotations
from dataclasses import dataclass
from pathlib import Path
import json
import re
from typing import List, Optional
INPUT = "book.txt" # input file with book text
OUT_DIR = Path("chapters")
OUT_DIR.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
# Looking for explicit chapters/parts. "Prologue" extracted separately.
CHAPTER_RE = re.compile(r"(?im)^\s*(chapter|part)\s+([0-9]+|[ivxlcdm]+)\b.*$")
# Explicit prologue heading (if present as a line)
PROLOG_RE = re.compile(r"(?im)^\s*prologue\b.*$")
# If no chapters found, split into fixed size parts
FALLBACK_PART_CHARS = 120_000
@dataclass
class Section:
index: int
title: str # for humans
heading: str # what will be voiced at the start of the file
text: str
def safe_slug(s: str, max_len: int = 60) -> str:
s = s.strip().lower()
s = re.sub(r"[^\w]+", "_", s, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
s = s.strip("_")
return (s[:max_len] if s else "section")
def normalize_preserve_paragraphs(t: str) -> str:
t = t.replace("\ufeff", "")
t = t.replace("\r\n", "\n").replace("\r", "\n")
# Collapse too many empty lines
t = re.sub(r"\n{3,}", "\n\n", t)
# Spaces/tabs within lines, but NOT line breaks
t = re.sub(r"[ \t]+", " ", t)
return t.strip()
def add_paragraph_pauses(t: str) -> str:
"""
Add pauses at paragraphs:
Double newline -> '.\n\n' (if no sentence ending before it).
"""
# normalize different "empty line" variants
t = re.sub(r"\n\s*\n", "\n\n", t)
# add period before paragraph if missing
t = re.sub(r"(?<![.!?…])\n\n", ".\n\n", t)
return t
def split_by_markers(lines: List[str], markers: List[int]) -> List[tuple[str, str]]:
# returns list of (title_line, body_text)
out = []
for k, start in enumerate(markers):
end = markers[k + 1] if k + 1 < len(markers) else len(lines)
title = lines[start].strip()
body = "\n".join(lines[start + 1:end]).strip()
if body:
out.append((title, body))
return out
def split_into_sections(text: str) -> List[Section]:
lines = text.split("\n")
# 1) find chapters/parts
chapter_markers = [i for i, line in enumerate(lines) if CHAPTER_RE.match(line.strip())]
# 2) if no chapters found, fallback
if not chapter_markers:
sections: List[Section] = []
raw = text
start = 0
idx = 1
while start < len(raw):
part = raw[start:start + FALLBACK_PART_CHARS].strip()
if part:
sections.append(Section(index=idx, title=f"Part {idx}", heading=f"Part {idx}.", text=part))
idx += 1
start += FALLBACK_PART_CHARS
return sections
sections: List[Section] = []
# 3) PROLOGUE: everything before first chapter
first_marker = chapter_markers[0]
before = "\n".join(lines[:first_marker]).strip()
# If this chunk has explicit word "Prologue" as a line, treat it as prologue.
if before:
sections.append(
Section(
index=1,
title="Prologue",
heading="Prologue.",
text=before
)
)
# 4) CHAPTERS
chapters = split_by_markers(lines, chapter_markers)
chapter_num = 1
for title, body in chapters:
sections.append(
Section(
index=len(sections) + 1,
title=title,
heading=f"Chapter {chapter_num}.",
text=body
)
)
chapter_num += 1
return sections
def main():
raw = Path(INPUT).read_text(encoding="utf-8", errors="ignore")
raw = normalize_preserve_paragraphs(raw)
raw = add_paragraph_pauses(raw)
sections = split_into_sections(raw)
print(f"Sections: {len(sections)}")
manifest = {
"input": INPUT,
"sections_dir": str(OUT_DIR),
"sections": [],
"total_chars": 0,
"total_utf8_bytes": 0,
"note": "Per-section counts include spoken heading and inserted paragraph pauses.",
}
for s in sections:
fname = f"{s.index:03d}_{safe_slug(s.title)}.txt"
path = OUT_DIR / fname
full_text = f"{s.heading}\n\n{s.text}".strip()
path.write_text(full_text, encoding="utf-8")
chars = len(full_text)
utf8_bytes = len(full_text.encode("utf-8"))
manifest["sections"].append({
"index": s.index,
"title": s.title,
"heading": s.heading,
"file": str(path),
"chars": chars,
"utf8_bytes": utf8_bytes,
})
manifest["total_chars"] += chars
manifest["total_utf8_bytes"] += utf8_bytes
print(f"[{s.index:03d}] {s.heading} -> {fname} | chars={chars} | bytes={utf8_bytes}")
(OUT_DIR / "manifest.json").write_text(
json.dumps(manifest, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2),
encoding="utf-8"
)
print("\nTotals:")
print(f" total chars: {manifest['total_chars']}")
print(f" total utf-8 bytes: {manifest['total_utf8_bytes']}")
print(f"Manifest: {OUT_DIR / 'manifest.json'}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()The result is a chapters/ folder with chapter files and a manifest.json containing info about all chapters: character count, bytes, etc.
Tool Problems
Of course wanted to do this for free. First step was searching for open source TTS engines.
Tried Silero TTS. Thanks to the maintainers of this project! But the quality didn’t work out. Reading was fine but at phrase boundaries the voice would drift. Anyone who remembers cassette tapes knows this sound when the player’s batteries were dying. That’s roughly how these transitions sounded.
Sighed and went looking for paid but affordable solutions.
Google Cloud Text to Speech
There are many services but the choice fell on Google Cloud Text to Speech because there was an unused credit sitting there.
To use the service you need to create an account, link billing, and enable the Cloud Text to Speech API.
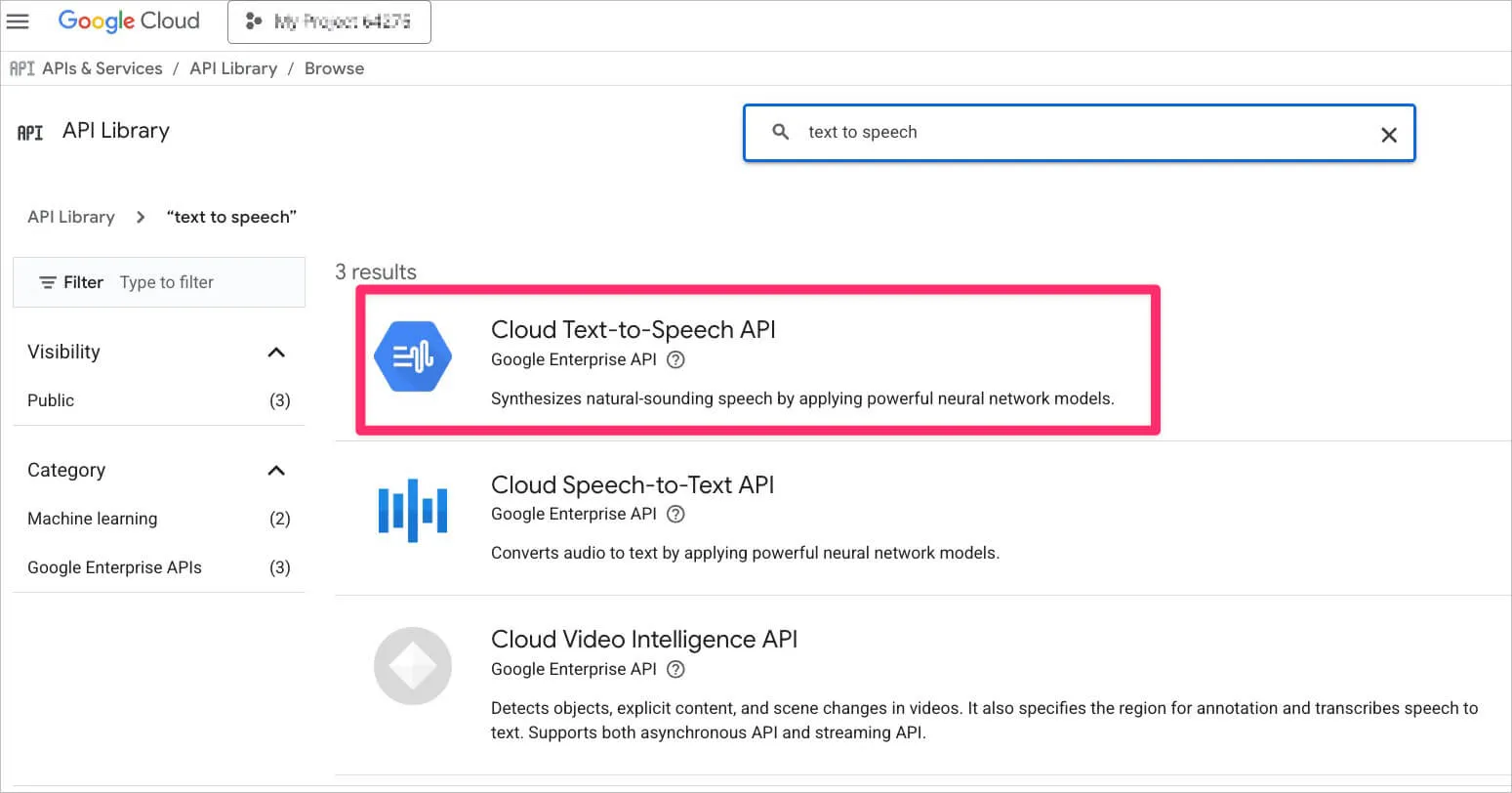
Make sure to study the pricing. Some voices cost $100+ per million characters. Studio quality wasn’t needed at this stage so the choice was affordable WaveNet voices. Listen to samples. Liked en-US-Wavenet-D (~$16 per million characters).
Authorization in gcloud CLI:
gcloud auth application-default loginAnd off to voicing.
Voicing Script
What matters in the voicing script:
- Split text into chunks of 5000 bytes (API limit). Important: bytes, not characters! For safety use
MAX_BYTES_DEFAULT = 4800. - Cut text at sentence boundaries (
[.!?…]), not random places. Too long sentences get split at spaces. - Save voiced chunks to a temp folder
tmp_audio_run/, clean it before voicing each chapter. - Concatenate chunks with ffmpeg. Fast and lossless.
- Output character and byte counts at the end for cost estimation.
Output format is mp3.
Google TTS voicing script
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from __future__ import annotations
from pathlib import Path
import argparse
import subprocess
import re
import shutil
from google.cloud import texttospeech
# ====== Google TTS settings (defaults) ======
LANG_DEFAULT = "en-US"
VOICE_DEFAULT = "en-US-Wavenet-D"
RATE_DEFAULT = 0.95
# Google limit is 5000 BYTES per request; keep margin.
MAX_BYTES_DEFAULT = 4800
SENT_CUT_RE = re.compile(r"([.!?…]+)\s+")
def split_sentences(t: str):
parts = SENT_CUT_RE.split(t)
out = []
for i in range(0, len(parts), 2):
chunk = parts[i].strip()
punct = parts[i + 1] if i + 1 < len(parts) else ""
s = (chunk + punct).strip()
if s:
out.append(s)
return out
def chunk_by_utf8_bytes(text: str, max_bytes: int):
sentences = split_sentences(" ".join(text.split()))
chunks = []
cur = ""
def fits(s: str) -> bool:
return len(s.encode("utf-8")) <= max_bytes
for s in sentences:
if not s:
continue
candidate = (cur + " " + s).strip() if cur else s
if fits(candidate):
cur = candidate
continue
if cur:
chunks.append(cur)
cur = ""
# single sentence too long -> split by words
if not fits(s):
words = s.split()
tmp = ""
for w in words:
cand = (tmp + " " + w).strip() if tmp else w
if fits(cand):
tmp = cand
else:
if tmp:
chunks.append(tmp)
tmp = w
if tmp:
chunks.append(tmp)
else:
cur = s
if cur:
chunks.append(cur)
return chunks
def ffmpeg_concat_mp3(tmp_dir: Path, output_mp3: Path):
subprocess.run(
["ffmpeg", "-y", "-f", "concat", "-safe", "0", "-i", "files.txt", "-c", "copy", "out.mp3"],
check=True,
cwd=str(tmp_dir),
)
output_mp3.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
(tmp_dir / "out.mp3").replace(output_mp3)
def main():
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="Generate MP3 from a text file using Google Cloud TTS (WaveNet) with safe UTF-8 byte chunking."
)
ap.add_argument("input", help="Path to input .txt file")
ap.add_argument("-o", "--output", help="Output .mp3 path (default: next to input file)")
ap.add_argument("--voice", default=VOICE_DEFAULT, help=f"Voice name (default: {VOICE_DEFAULT})")
ap.add_argument("--lang", default=LANG_DEFAULT, help=f"Language code (default: {LANG_DEFAULT})")
ap.add_argument("--rate", type=float, default=RATE_DEFAULT, help=f"Speaking rate (default: {RATE_DEFAULT})")
ap.add_argument("--max-bytes", type=int, default=MAX_BYTES_DEFAULT, help=f"Max UTF-8 bytes per request (default: {MAX_BYTES_DEFAULT})")
ap.add_argument("--tmp-dir", default="tmp_audio_run", help="Temporary directory for mp3 chunks (default: tmp_audio_run)")
ap.add_argument("--clean", action="store_true", help="Delete temp directory before run")
args = ap.parse_args()
input_path = Path(args.input)
if not input_path.exists():
raise SystemExit(f"Input not found: {input_path}")
out_path = Path(args.output) if args.output else input_path.with_suffix(".mp3")
tmp_dir = Path(args.tmp_dir)
if args.clean and tmp_dir.exists():
shutil.rmtree(tmp_dir)
tmp_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
text = input_path.read_text(encoding="utf-8", errors="ignore").strip()
if not text:
raise SystemExit("Input file is empty.")
parts = chunk_by_utf8_bytes(text, args.max_bytes)
if not parts:
raise SystemExit("No chunks produced (unexpected).")
client = texttospeech.TextToSpeechClient()
voice = texttospeech.VoiceSelectionParams(language_code=args.lang, name=args.voice)
audio_cfg = texttospeech.AudioConfig(
audio_encoding=texttospeech.AudioEncoding.MP3,
speaking_rate=args.rate,
)
filelist = []
total_chars = 0
total_utf8_bytes = 0
for i, part in enumerate(parts, 1):
b = len(part.encode("utf-8"))
if b > args.max_bytes:
raise SystemExit(f"Chunk {i} too big: {b} bytes (max {args.max_bytes})")
total_utf8_bytes += b
total_chars += len(part)
resp = client.synthesize_speech(
input=texttospeech.SynthesisInput(text=part),
voice=voice,
audio_config=audio_cfg,
)
fname = tmp_dir / f"part_{i:04d}.mp3"
fname.write_bytes(resp.audio_content)
filelist.append(fname)
if i % 25 == 0 or i == len(parts):
print(f"Parts: {i}/{len(parts)}")
(tmp_dir / "files.txt").write_text(
"\n".join(f"file '{f.name}'" for f in filelist),
encoding="utf-8"
)
ffmpeg_concat_mp3(tmp_dir, out_path)
print(f"Done: {out_path}")
print(f"Chunks: {len(parts)}")
print(f"Total chars sent: {total_chars}")
print(f"Total utf-8 bytes sent: {total_utf8_bytes}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Voicing Chapters
Run the script for each chapter:
python gcloud_tts_file.py chapters/001_prologue.txt -o audio/001_prologue.mp3 --cleanFlags:
--cleanclears the temp folder before running-osets the output mp3 path
The script has other flags too. Adjust as needed.
Result is an audio file for each chapter.
Profit!
Had a great time figuring all this out. And ended up listening to the book =)
Cost
The book was free: stayed under 1 million characters and fit within the WaveNet free tier.
Room for Improvement
Robot Narrator
Be prepared: this is not a human narrator. The voicing will have many wrong stresses, pronunciations, and intonations.
To judge the quality, a short sample:
For fiction this approach didn’t work for me personally. Ended up switching to audiobooks in English. There’s a saying about two chairs: either a robot narrator in your native language, or a brilliant narrator in English.
But for technical literature that has no audio version this is a great approach.
Text Markup
Ideally send not txt but SSML for voicing. That allows control over pauses, stresses, and speed. But that’s the next level. This time there was no time or desire to go deeper.
Interface
For now all commands run manually in the terminal. At the early stage that’s fine for debugging. Once the flow stabilizes will build a single interface: one window where you drop the book file and get a player with audio on the output.
Single File
This time worked with each chapter separately and that was justified. Next time will automate all intermediate steps. In the end will merge everything into a single m4b file with chapters and cover art. Like the pros do =)